Starting an e-commerce business is the dream of most people because there is no need for a physical store, and you can get more profit through it.
An e-commerce business is profitable, but it is necessary to know a little about it before starting; otherwise, the chances of failure are higher.
Through this article, you’ll learn the steps to start an e-commerce business, how much it costs, and extra tips on how to build a customized website within your budget.
Steps to Start an E-commerce Business
- Research a Profitable Product
- Find a Reliable Supplier
- Pick an E-Commerce Platform
- Set-up Your E-Commerce Store
- Get a Payment Gateway
- List out the products on the E-commerce Store
- Marketing Your Stores to Boost Your Sales
Research a profitable product
The first step in starting an e-commerce business is to find a profitable product. As you brainstorm innovative ideas, ensure there is sufficient customer support, as without it, there can be no business.
Before choosing a product do research on market trends and consider the following
What products are in high demand within your niche?
What is the potential market size for your product?
How does your product differ from those already on the market?
Analyzing your competitors through customer reviews is an effective strategy for identifying gaps in their offerings and a better understanding of customer needs. This approach will help you fill those gaps with your products.
Focus on products with growing demand rather than those driven by short-term trends. Always choose products that have strong demand and minimal competition.
Find a Reliable supplier
Once you have identified your product, the next step is to find a reliable supplier. Consider the following steps to identify your supplier:
- Identify your product requirements by clearly defining your product specifications, quality standards, and desired features.
Explore Sourcing Options:
1. Resell Existing Products
You can research the popular products on the marketplace like Amazon and eBay. Look for products with high demand and low competition.
2.Dropshipping
You can partner with dropshipping or print-on-demand services to provide a wide range of products without holding inventory. To differentiate your offering, you can customize products with your design or branding.
3. Work with manufacturers
You can also develop your own products by creating designs, prototypes, and specifications. Evaluate manufacturers based on their capabilities, quality standards, and ability to meet your requirements.
- Check Supplier Credibility: Check supplier profiles, reviews, and response rates to analyze their reliability. Request a sample or prototype of your product to evaluate the quality.
- Negotiate Terms and Pricing: Negotiate costs with suppliers to get the best profit margins for your business.
Pick an e-commerce platform
Choosing the right e-commerce platform is very important for the success of your online store. There are a few things we should consider when selecting an e-commerce platform
- Your Budget
- The size of your Inventory
- Need for features such as POS or Multichannel selling
Some best Platforms
1.Woo Commerce
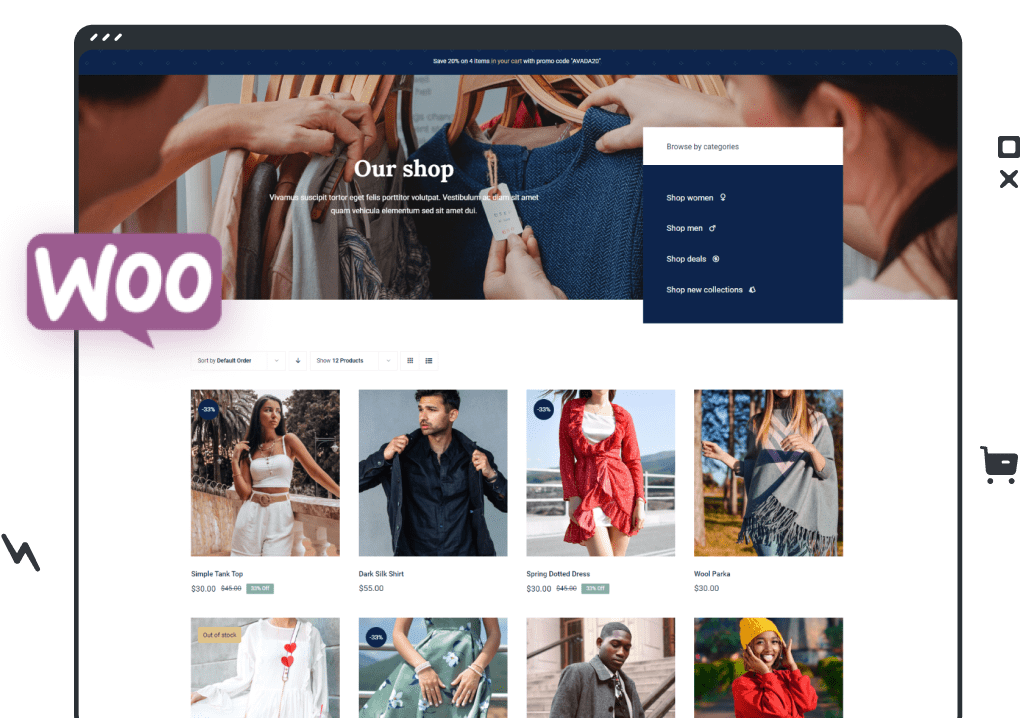
WooCommerce is perfect for businesses that already have a WordPress site and require a highly customizable solution. It’s ideal for those selling a variety of products, including physical goods, digital downloads, and services.
Pros
- WooCommerce is developed as a core plugin, which is free and is therefore advantageous to any startup business. However, there could be extra charges depending on your hosting, themes, and extensions.
- Since WooCommerce has an open-source format, it permits users to customize their store design and features.
- The platform WooCommerce is based on WordPress and has advanced SEO features, ensuring better visibility of the store.
Cons
- WooCommerce can be quite complex for new users, especially those with limited experience in WordPress.
- Compared to other platforms, WooCommerce does not offer personal customer support, which may not suit everyone.
- Hosting and domains are handled independently by the users, and this can complicate things.
2. Shopify
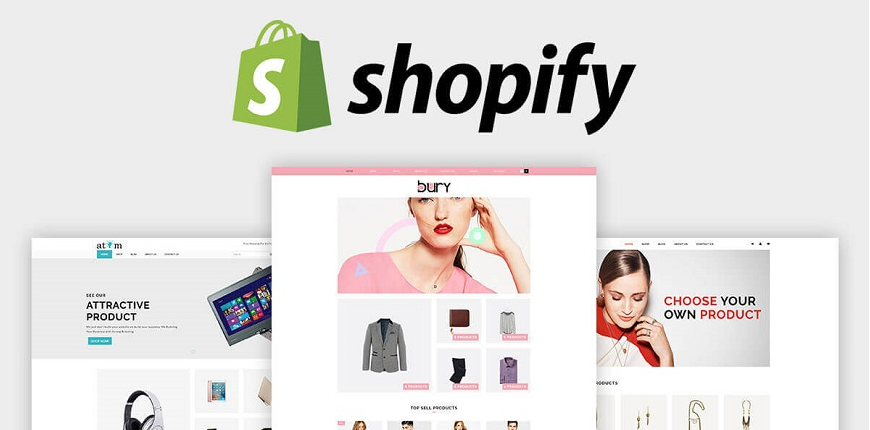
Shopify is an excellent choice for small and medium-sized businesses that need an easy-to-use and comprehensive platform with e-commerce capabilities. It is ideal for those who want to quickly launch their site without needing extensive technical knowledge.
Pros
- It is a highly user-friendly platform that allows individuals and companies to build an online store even without knowledge of coding.
- It provides hosting, a payment gateway, and numerous applications to extend its functionalities and easy setup.
- Shopify offers effective customer care with both live chat and phone support.
Cons
- Transaction fees are charged if you choose a payment gateway other than Shopify Payments.
- It comes with different themes; however, the customization is limited as compared to the open-source options like WooCommerce.
3. Odoo
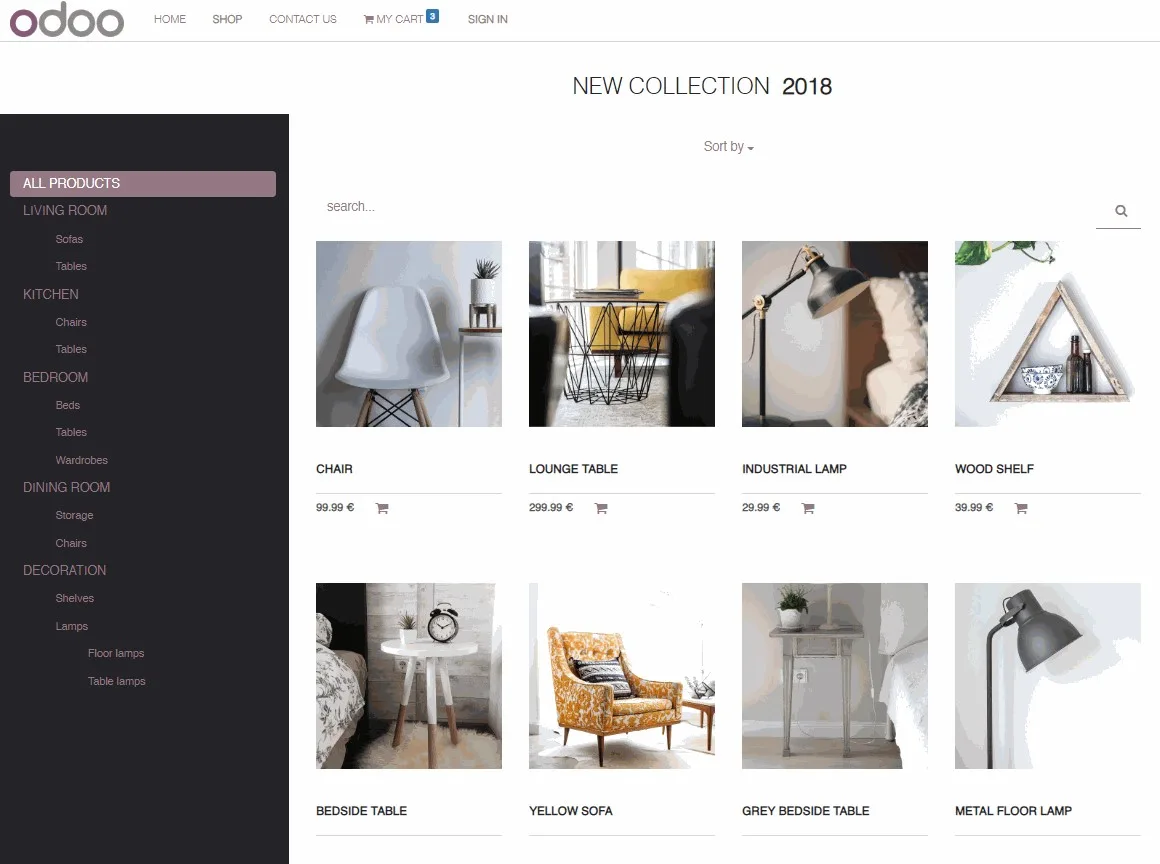
Odoo is ideal for larger businesses or organizations or those business operations that are quite complex and involve interaction with other business processes. It’s useful for companies that need to handle several operations, from e-commerce to customer relationship management.
Pros
- It is a perfect fit for companies that need an integrated solution for customer relationship management, inventory management, accounting, and other modules.
- Odoo is highly customizable, making it easy to build a site according to your business requirements.
- It can be scaled up as your business expands in terms of functionality and workload to handle more complexities as it expands in functionality.
Cons
- Odoo implementation can be problematic, especially for users unfamiliar with ERP systems.
- The community version is open source, so it is free, while the enterprise versions may become costly with additional features and more users.
- Users may need some time to learn how to navigate and use the different applications effectively.
Set up your E-commerce store
After selecting a platform, you need to set up your online store. Here are some important steps in setting up your store.
Purchase a Domain Name
Your domain name is your web address; therefore, you must choose the most appropriate one that defines your brand and is easy to memorize. You can acquire a domain from your e-commerce solution supplier or a domain name supplier. Do not make the name too raw and long to pronounce; it should be easy to spell and contain the business keywords if possible.
Designing
The appearance of the e-commerce store can grab attention and ensure that the user converts into a customer. Most platforms offer customizable templates that can be modified to suit your brand.
- Ensure your website is user-friendly by creating a clear menu and a simple checkout process to avoid confusing visitors.
- Provide high-quality images with strong contrast and a consistent color palette that aligns with your brand identity.
- Make sure your design is mobile-responsive, as a large number of people use their mobile phones for online shopping.
Establish Shipping Options
Decide how you will manage shipping, as it is crucial for running an e-commerce store. Consider the following:
Shipping Methods
Choose between normal, express, or international delivery according to your target customer.
Shipping Costs
Decide whether to make shipping free, charge a standard fee, or charge according to location or product weight. Most e-commerce platforms allow customers to estimate the shipping charges at the time of ordering through various tools.
Fulfilment Options
Decide between your own shipping or collaborating with third-party fulfilment companies. Some platforms enable it to connect with fulfilment centres to simplify the process.
Returns Policy
Explain your returns policy in detail to gain the customers’ confidence as well as minimise any disputes that may occur.
Implement Security Measures
Security is very important in e-commerce to enhance the safety of the customer’s information. Key measures include:
SSL Certificate
Make sure your website has an HTTPS prefix to encrypt information shared between your website and the customers.
Payment Security:
Make sure to use the appropriate payment gateways that support the PCI DSS compliance to ensure that the transactions are strictly secure.
Regular Updates:
Update your platform, plugins, and themes regularly in order to avoid the attack of such vulnerabilities.
Get a payment gateway
Payment gateway integration is a crucial step in setting up your e-commerce store, as it enables you to process online transactions securely. Select a gateway that can accept several forms of payment, including credit/debit cards and PayPal, among others, and one that can integrate with your e-commerce software. Some of the best ones include Stripe PayPal and Square.
List out the products on the e-commerce store
With your e-commerce store ready, it is time to list your products for customers. Begin with the writing of clear and specific descriptors of products, including their attributes, advantages, and characteristics. Use high-quality images to showcase your products from multiple angles, ensuring they are visually appealing. Make sure to include useful keywords for your products and services in your titles and descriptions to enhance search engine optimization. Create categories to help customers find what they’re looking for more quickly, and set up an inventory control system to track your products and ensure you sell only what you have in stock. This will go a long way in helping you to offer your customers a smooth shopping experience.
Marketing your stores to boost your sales
To effectively market your e-commerce store and boost sales, implement a combination of strategies that target both new and returning customers. Begin with Search Engine Optimization (SEO) to increase your website’s ranking on the search engine result page. Market through social channels like Instagram and Facebook using both organic promotional posts and paid/sponsored advertisements. Email marketing is also important; make a list of subscribers to send them special offers, updates on new products, and notifications about backordered items. Consider using pay-per-click advertising to quickly drive visitors to your site. It is evident that alongside these strategies you build an integrated marketing approach that brings traffic, more conversions, and consumers’ loyalty.
Remember, starting an e-commerce business is a journey, and it may take time to find the right formula for success. Be patient, adaptable, and always focused on providing value to your customers.
How much does it cost to start an e-commerce business?
Many people find it appealing to start an e-commerce company because one can earn big money with relatively low capital costs. However, it is essential to determine the costs before starting the project.
1. Domain name

The cost of a domain name depends on its availability and the extension you choose (.com,.co.uk,.in). The cost of the usual domain is likely to be in the range of £3–£20 per year. Premium domain names may often be more expensive.
2. Hosting

Web hosting is crucial since it determines the availability of your e-commerce site on the internet. The price will fluctuate between £ 100 and £ 2 000 per year, all depending on the sort of host you give preference to (shared, VPS, or devoted) and the resources required for your website. For small to medium-sized businesses, a budget of around £200 and £500 annually will be sufficient.
3. E-Commerce Platform
Selecting the correct e-commerce platform is crucial to your business. Platforms like Shopify or WooCommerce have basic monthly subscription packages ranging from £20 to £300. If you are seeking a more specific solution, you might look into solutions like Magento, which, while being more expensive in terms of initial setup, does provide almost limitless functionality.
4. Website Development
Designing and developing your e-commerce site can be one of the largest expenses for your business. The costs start from £1000 for a simple website and can exceed £10000 for a custom website. The average cost to design and develop a small to midsized B2C e-commerce website, including UX/UI design, ranges from £5,000 to £20,000.
5. Shipping
Shipping expenses will vary depending on the type of product needed to be shipped and the shipping method. You may need to budget for shipping materials, logistics, and fulfilment services. Initial shipping costs may range from £100 to £500 and can vary depending on your business model and shipping volume.
6. Payment Gateway
It is crucial to use a payment gateway to complete transactions securely. Payment gateway fees are usually charged on a per-transaction basis plus a monthly rate. You will probably be charged £20 to £50 per month and transaction costs that may be around 1.4% to 3% per transaction, depending on the provider.
7. Marketing
Marketing is beneficial in creating awareness of your e-commerce website amongst its targeted consumers. Marketing costs depend on the overall marketing approach you’ll be using. Your initial budget could range from £500 to £5,000 in the first few months to cover social media ads, Google organic ranking, pay-per-click campaigns, and SEO services.
If you’re looking for a budget-friendly solution for your e-commerce website, consider partnering with Lowcostwebsitesandstores . As a leading website development company in the UK, they offer various services, including web hosting, design, development, and SEO, all at competitive prices. With their expertise and commitment to delivering high-quality results, you can confidently launch your e-commerce business and stay within your budget.

